Autocomplete is a feature in ecommerce search that provides real-time suggestions based on the user’s input.
This technology, popularized by platforms like Google, streamlines the search process, aiding in form filling and information retrieval.
So, what is autocomplete?
The term “autocomplete” comes from its ability to complete a form or query automatically, without the user needing to type everything out.
In addition to helping users complete forms, autocomplete can save time and effort by predicting what a user wants to search for next. Let’s say you are interested in computer accessories.
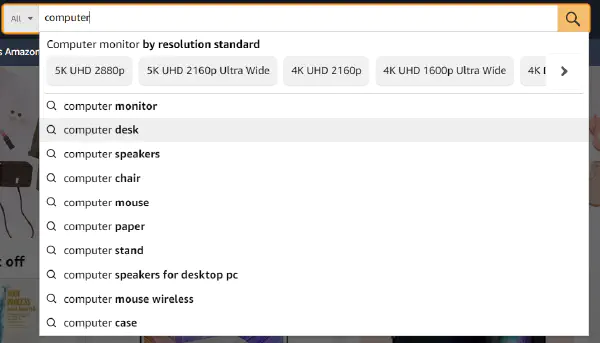
Let’s take Amazon as an example. By starting to type “computer” into the search, it automatically suggests possible query endings, such as “computer desk,” “computer mouse,” etc.
Predictive search, an autocomplete extension, uses previous queries to forecast future search terms. This feature adapts to user patterns, enhancing the search experience by suggesting relevant terms and products [1].
For example, if you search for the “best laptop,” the system will know that you are currently interested in laptops. So it will suggest different brands and models you might be interested in.
Later, the ecommerce search might also suggest relevant appliances like a laptop case or a portable mouse.
How does the autocomplete function help the user?
Autocomplete significantly simplifies the search process. Predicting and completing queries reduces typing time, minimizes errors, and enhances the probability of finding the desired results.
For example, in an e-shop setting, typing “sneakers” might immediately suggest categories like “women’s sneakers,” “running shoes,” or specific brands, reflecting the system’s nuanced understanding of user intent [2].
This predictive capability ensures that users are presented with the most relevant shopping options quickly and efficiently.
Creating an Effective Predictive Search Experience
With the increasing use of mobile devices, businesses are adopting predictive search technologies. To create a useful experience, consider the following:
Accuracy of Predictions: Ensure your system’s predictions are relevant and accurate. Inaccurate predictions can lead to user confusion and reduced conversion rates [4].
Usability Impacts: Predictive search should enhance, not hinder, the user experience. The system’s suggestions must align with the user’s intent to avoid misdirection [5].
Optimization for Conversions: Analyze site content to include frequently associated terms in autocomplete predictions. This tailored approach can improve user engagement and conversion rates.
Implementing Autocomplete Search Effectively
When implementing autocomplete search, it’s critical to choose the right technology and test predictions thoroughly, possibly through A/B testing. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of predictions based on real-time performance data will ensure the system remains effective and user-friendly.
In conclusion, autocomplete and predictive search technologies are powerful tools for enhancing user experience and search efficiency. Their implementation, however, must be carefully managed to ensure accuracy, relevance, and user satisfaction.
By understanding the intricacies of these technologies and continuously refining them, businesses can significantly improve their users’ search experiences.
Stay ahead of the market with LupaSearch
Interested in elevating your platform’s search capabilities?
Consider Lupa Search’s innovative ecommerce search solutions.
We offer an internal audit option to assess and optimize your current site search functionalities. Alternatively, you can apply for a demo to experience firsthand how LupaSearch can transform your search experience with advanced autocomplete and predictive search technologies.
Explore these options to ensure your search tools are not just functional but exceptional.
References
Chonka, P., Diepeveen, S., & Haile, Y. (2022). Algorithmic power and African indigenous languages: search engine autocomplete and the global multilingual Internet. Media, Culture & Society, 45, 246 - 265. https://doi.org/10.1177/01634437221104705.
Patel, R., Sheth, S., & Kelkar, K. (2016). Autocomplete Text using Graph Database. International Journal of Computer Applications, 144, 42-45. https://doi.org/10.5120/IJCA2016910509.
Lehmann, F., & Buschek, D. (2020). Autocompletion as a Basic Interaction Concept for User-Centered AI. . https://doi.org/10.18420/muc2020-ws111-328.
Ward, D., Hahn, J., & Feist, K. (2012). Autocomplete as a research tool: A study on providing search suggestions. Information Technology and Libraries, 31, 6-19. https://doi.org/10.6017/ITAL.V31I4.1930.