The European Union’s digital marketplace has witnessed substantial growth, allowing businesses to tap into a vast and solvent audience. In 2022, the e-commerce user base in the EU impressively reached 523 million [1].
However, navigating the EU market comes with its set of regulations, notably the Omnibus Directive (EU) 2019/2161, effective from May 2022 [2].
This legislative framework aims to fortify consumer protection by modernizing existing laws to better fit the digital age, impacting e-commerce businesses significantly.
Understanding the Omnibus Directive
The Omnibus Directive serves as a cornerstone in the EU’s effort to strengthen consumer laws.
It addresses modern ecommerce businesses that use new-age ecommerce practices: paid advertisements, customer reviews, personalized product ranking, product boosting, etc., ensuring businesses operate transparently and fairly online.
So, what changes are most relevant to your ecommerce business?
Key Impacts on E-commerce Businesses
1. Prohibition of Fake Reviews
The regulation prohibits the usage of fake customer reviews in an ecommerce store. In addition, businesses that publish consumer reviews must provide their customers with information on how they ensure that these reviews come from legitimate consumers.
2. Transparent Pricing and Discount Policies
It introduces clear rules on discounting practices, requiring businesses to display the previous price of products before applying discounts, ensuring that price reductions are authentic and transparent.
The previous price refers to the lowest price at least 30 days before the price reduction. In the case of a gradual price reduction, the previous price is the price before the first price reduction.
3. Criteria for Product Ranking Disclosure
E-commerce platforms must disclose the basis of product rankings in search results, including if rankings are influenced by paid advertisements, and promoting transparency in product listings.
4. Personalized Pricing Disclosure
Ecommerce businesses now have to transparently indicate the criteria they use to rank products.
If your consumers can search for products offered by different sellers, you must indicate the criteria that determine the ranking of the products provided to the consumer as a result of his search query.
For example, as a retailer, you must state the basis on which the products are ranked: price, ratings of customers, or a combination of several factors.
If the ranking of a product in search results is based on paid advertising or other payments received from the sellers, this information should also be disclosed to consumers.
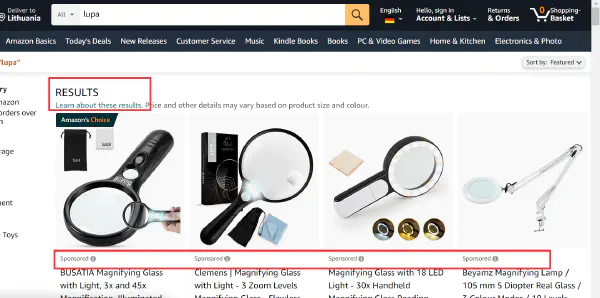
Example in Amazon.de
Conclusion
E-commerce businesses must adhere to these regulations to not only comply with EU law but also to build trust and credibility with their consumer base. Note that individual consumers have a right to get direct compensation for unfair commercial practices of the entities.
That is why it is crucial to follow the directive requirements when working with shoppers in the EU.
After all, a 500-million market of buyers with high purchasing power is worthy of your business attention. Applying the correct practices to your e-shop will open up huge selling opportunities in the European Union market.
References
Stephanie Chevalier. Number of B2C e-commerce users in Europe from 2017 to 2027. Jul 13, 2023. Statista. https://www.statista.com/forecasts/715683/e-commerce-users-in-europe.
Directive (EU) 2019/2161 of the European Parliament. PE/83/2019/REV/1. OJ L 328, 18.12.2019, p. 7–28. http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/2161/oj.